Goal
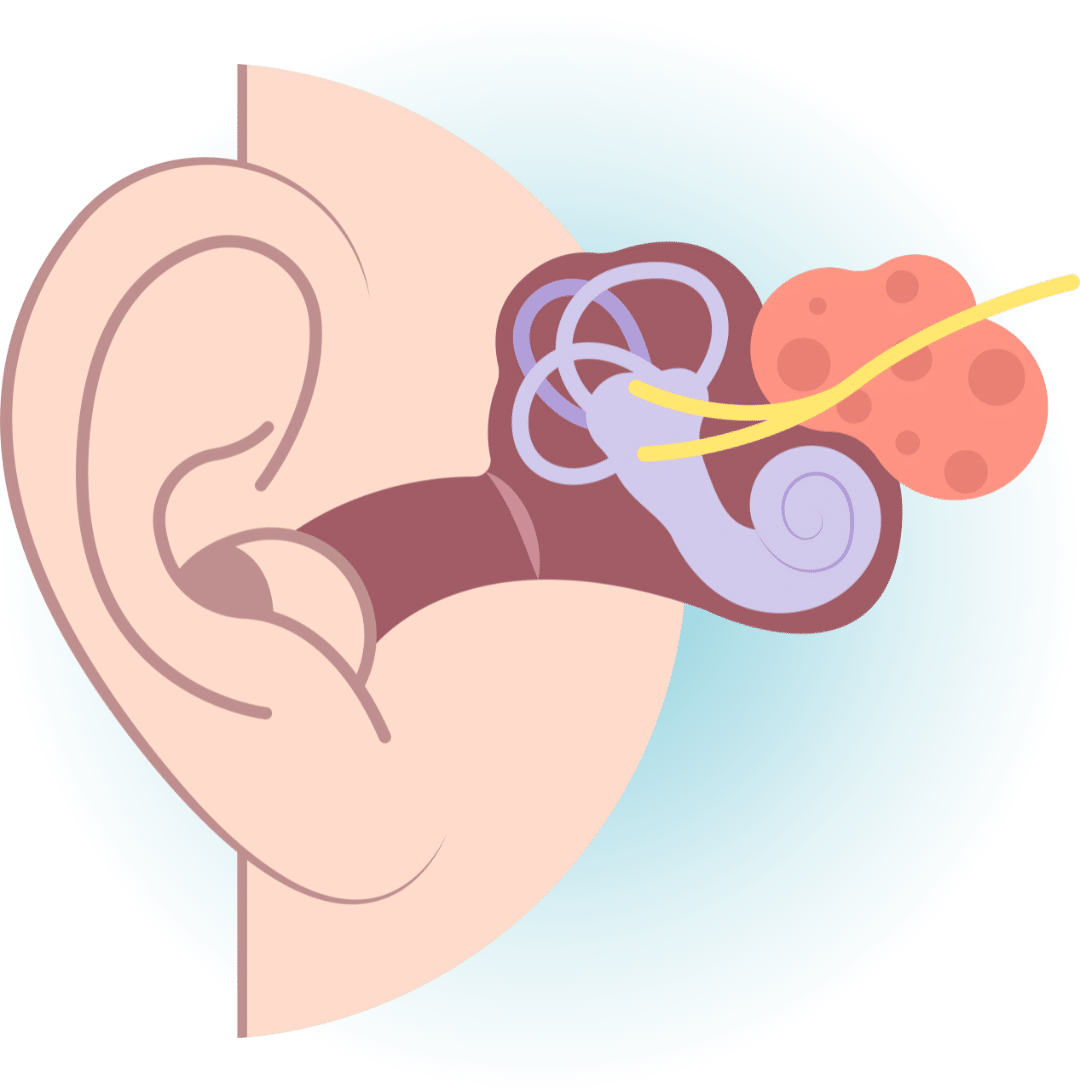
The primary goal of Vestibular Rehabilitation Therapy (VRT) is to retrain the brain to compensate for vestibular dysfunction. This therapy aims to improve balance, reduce dizziness, and stabilise gaze, helping patients regain control over their daily activities.
Common conditions VRT treats
- Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV)
- Ménière’s Disease
- Labyrinthitis and Vestibular Neuritis
- Vestibular Migraine
- Presbyvestibulopathy (Age-related vestibular dysfunction)
- Persistent Postural Perceptual Dizziness (PPPD)
- Concussion or mild Traumatic Brain Injury
- Stroke
- Cervicogenic dizziness
Exercises in VRT
VRT consists of specialised exercises aimed at promoting adaptation, habituation, and substitution, enabling the brain to adjust to new patterns of sensory input.
Adaptation Exercises: These exercises help recalibrate the brain to new vestibular signals through repeated head and eye movements, restoring gaze stability.
Habituation Exercises: Designed to reduce the brain’s sensitivity to movements that trigger symptoms, these exercises gradually expose patients to those movements.
Balance Training: Focused on enhancing stability and coordination, balance training involves targeted exercises that challenge balance in various positions, including standing, walking, and turning.
Gaze Stabilisation Exercises: These exercises assist patients in controlling eye movements, improving their ability to keep their eyes focused during head movements.
Goal
The gold standard treatment for Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV), this technique aims to help reposition displaced calcium crystals (otoconia) in the inner ear to alleviate symptoms.
Common conditions treated by Canalith Repositioning Maneuvers
- Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV)
Details of the Canalith Repositioning Maneuvers
- Epley Maneuver: A series of specific head movements to guide the displaced crystals back to their proper location in the inner ear.
- Semont Maneuver: Involves moving the patient quickly from lying on one side to the other to reposition the crystals.
Goal
To strengthen muscles, improve coordination, and increase proprioception (awareness of body position), enhancing posture and reducing the risk of falls while improving confidence in mobility.
Common conditions treated by balance & posture training
- Balance disorders
- Generalised dizziness
- Fall risk in older adults
Exercises in balance & posture training
- Strengthening Exercises: Focused on core and lower body strength to support stability.
- Balance Exercises: Activities like single-leg stands or balance boards to challenge and improve coordination.
- Posture Correction Exercises: Techniques to enhance alignment and body awareness during daily activities.
Goal
To reduce the fear of falling or moving due to dizziness, empowering patients to engage in activities without anxiety.
Common conditions treated by improving confidence in mobility
- Anxiety related to vestibular disorders
- Dizziness-induced fear of movement
Exercises to improve confidence in mobility
- Gradual Exposure Activities: Slowly introducing movements that trigger fear while providing support.
- Simulated Mobility Tasks: Practicing walking and turning in safe environments to build confidence.
Goal
To help patients regain independence in their everyday routines and avoid symptoms like dizziness when performing specific movements.
Common conditions treated by functional training
- Vestibular disorders
- Post-concussion symptoms
- Age-related functional decline
Exercises in functional training
- Task-Specific Exercises: Simulating daily activities, such as reaching or bending, to enhance functional performance.
- Dynamic Balance Training: Incorporating movements like walking and reaching to improve coordination during daily tasks.