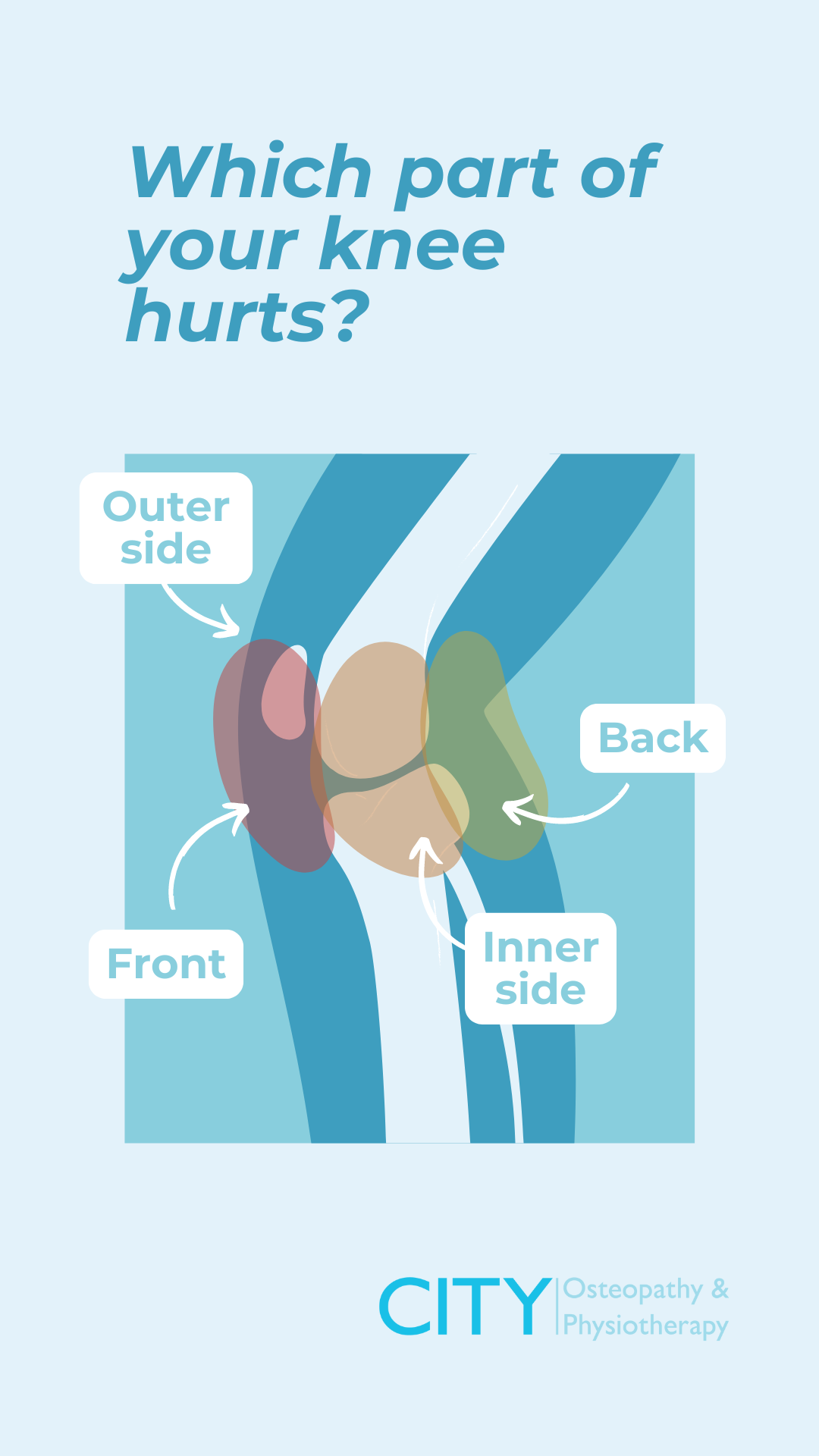
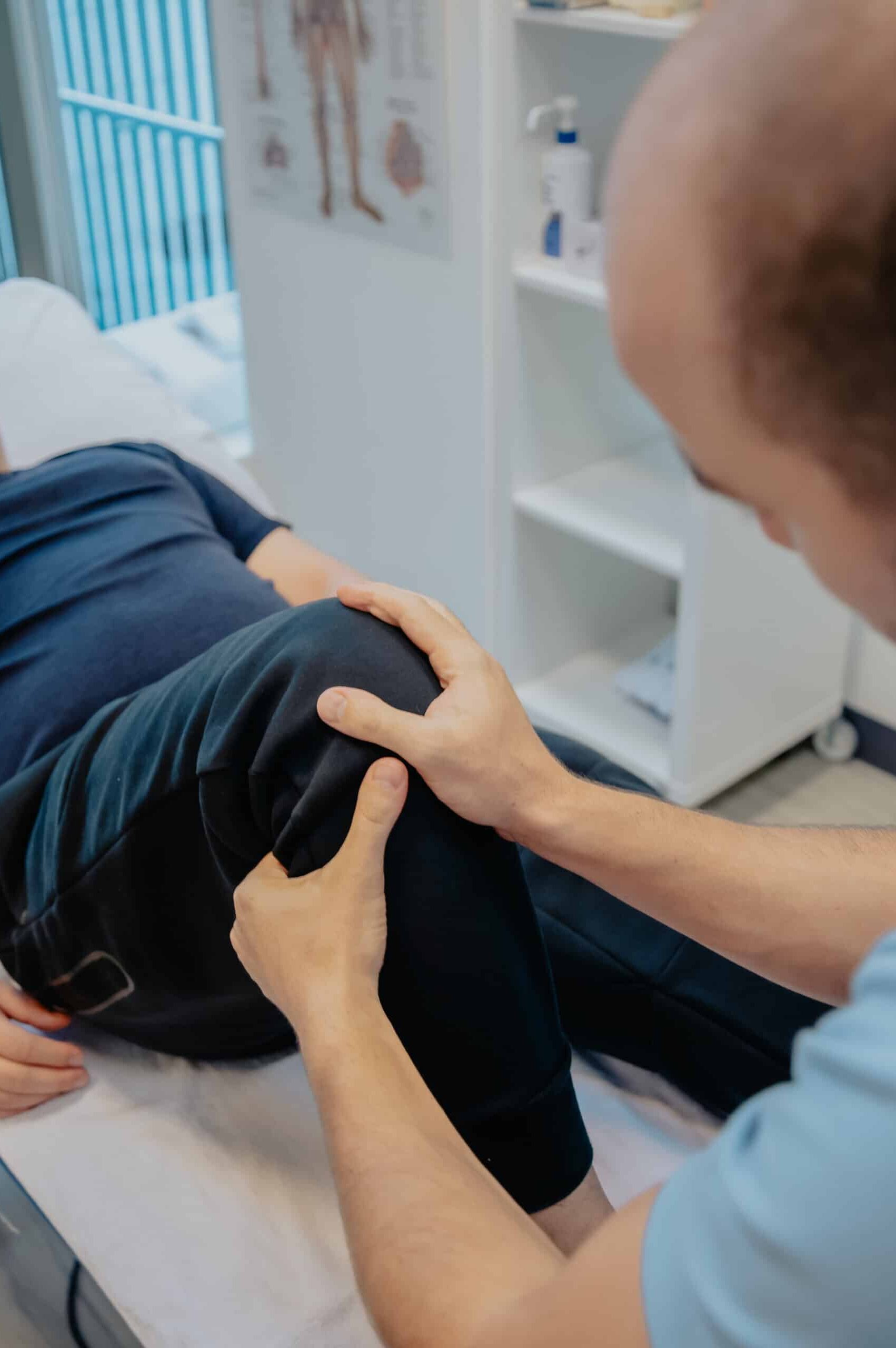
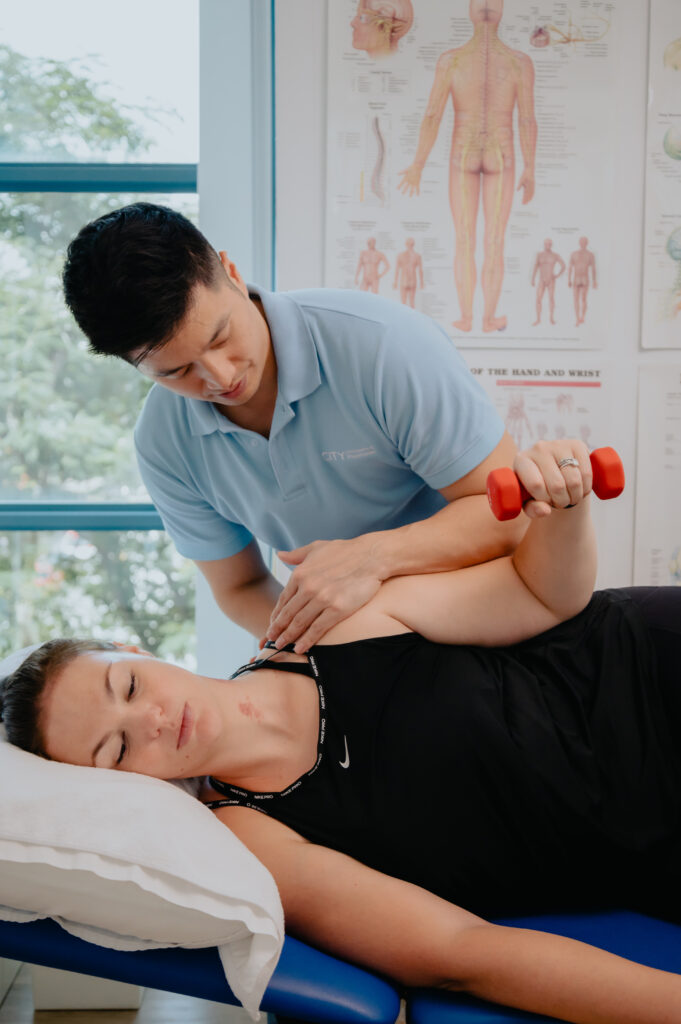
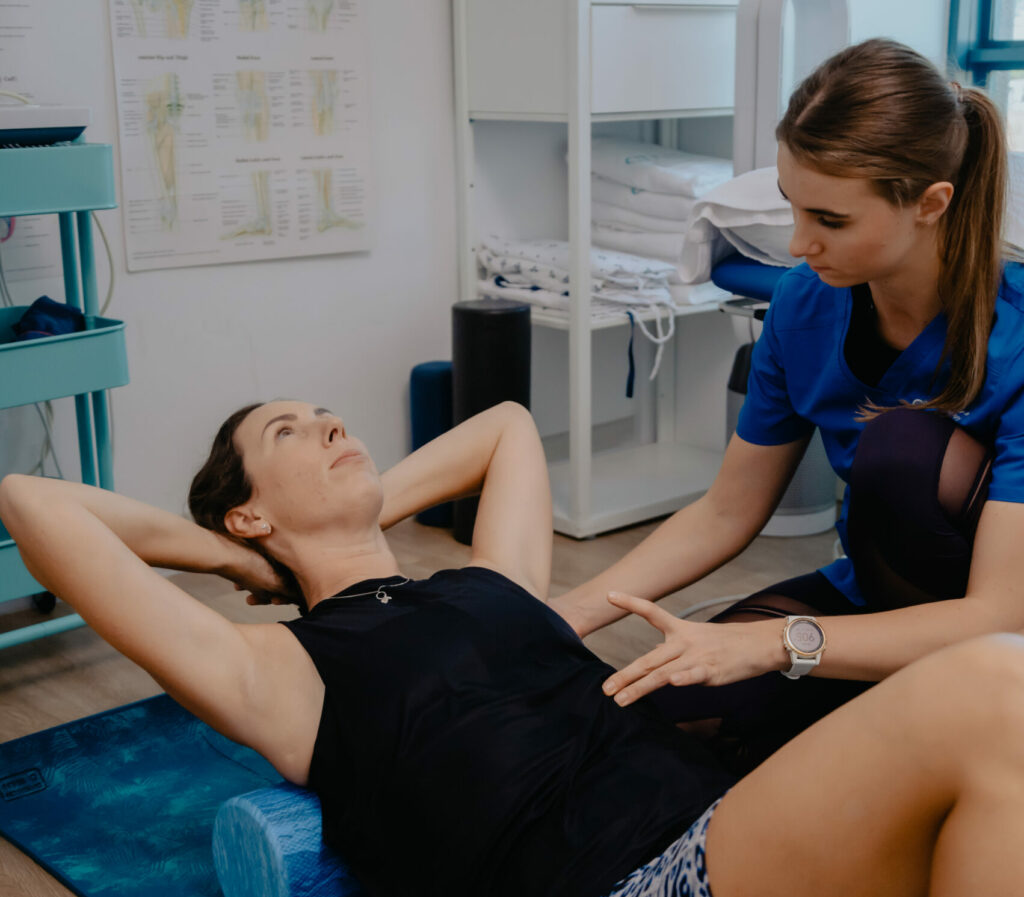
Ignoring knee pain or delaying treatment can lead to worsening conditions and longer recovery times. Early intervention is key to feeling better sooner. By seeking professional help, you can reduce pain and inflammation, improve knee function and mobility, and prevent further injury.
Addressing knee pain early ensures you can continue enjoying your daily activities without discomfort. Our team at City Osteopathy and Physiotherapy is here to provide the care and support you need for a healthier, pain-free life. Don’t wait—let us help you get back to doing what you love.